Navigating the labyrinth of credit scores can be daunting, but understanding the FICO Score 8 is essential for financial literacy. This comprehensive guide will demystify the FICO Score 8, elucidating its nuances and significance in the broader context of personal finance.

Taking in Credit Scores: A Brief Overview
Credit scores are numerical representations of an individual’s creditworthiness, calculated based on their credit history. These scores range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating lower credit risk. Lenders use these scores to assess the likelihood of a borrower repaying loans.
The Evolution of FICO Scores
The FICO scoring system has evolved significantly since its inception in 1989. Each iteration aims to improve accuracy and predictability. The FICO Score 8, introduced in 2009, reflects modern credit behaviors and economic conditions, making it more relevant for today’s credit landscape.
Why FICO Score 8 Was Introduced
The introduction of FICO Score 8 addressed several limitations of previous versions. It incorporated new data points and refined algorithms to better predict borrower risk. This iteration aimed to offer a more nuanced assessment of credit behavior, thus enhancing lenders’ decision-making processes.
Key Features of FICO Score 8
FICO Score 8 includes several innovative features. It places greater emphasis on high balances and penalizes isolated late payments less harshly. This approach ensures a more balanced evaluation, capturing both positive and negative credit behaviors effectively.
Differences Between FICO Score 8 and Previous Versions
While previous FICO scores focused heavily on payment history, FICO Score 8 introduced a more balanced consideration of credit utilization and the impact of recent credit behavior. It also offered a more lenient view on minor late payments and isolated incidents.
Impact of FICO Score 8 on Credit Decisions
Lenders using FICO Score 8 benefit from enhanced predictability and risk assessment. This score helps in making informed decisions regarding loan approvals, interest rates, and credit limits, ultimately leading to better financial outcomes for both lenders and borrowers.
Factors Influencing FICO Score 8
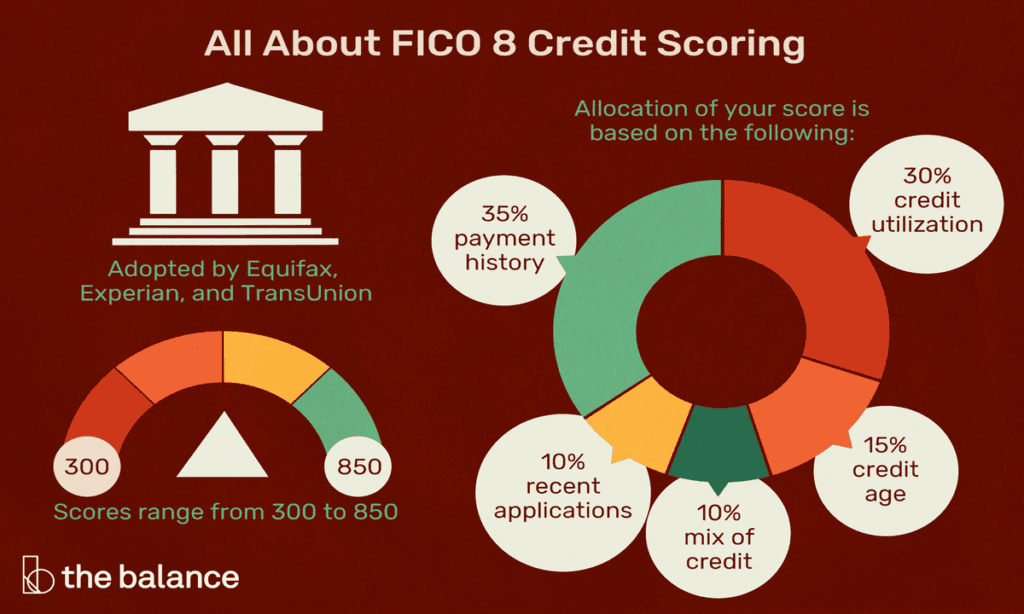
FICO Score 8 evaluates five primary factors: payment history, credit utilization, length of credit history, new credit, and credit mix. Each factor contributes differently to the overall score, providing a comprehensive picture of a borrower’s creditworthiness.
Payment History: The Cornerstone of Your Score
Payment history is the most influential factor, comprising 35% of the score. Consistent, on-time payments boost scores significantly, while missed or late payments can severely damage it. Maintaining a flawless payment record is paramount.
Credit Utilization: Balancing Your Debt
Credit utilization, accounting for 30% of the score, measures the ratio of credit card balances to credit limits. Lower utilization rates indicate responsible credit management, positively impacting the score. Aim to keep utilization below 30%.
Length of Credit History: The Longer, the Better
The length of credit history contributes 15% to the FICO Score 8. Longer credit histories generally enhance scores, as they provide more data on credit behavior. Keeping older accounts open can benefit your score over time.
New Credit: The Risks of Recent Inquiries
New credit inquiries and accounts make up 10% of the score. Multiple inquiries in a short period can signal financial distress, negatively affecting the score. Limiting new credit applications can help maintain a healthy score.
Credit Mix: The Variety of Credit Accounts
Credit mix, also 10% of the score, evaluates the diversity of credit accounts, including credit cards, mortgages, and installment loans. A varied credit portfolio indicates adept credit management, positively influencing the score.

How FICO Score 8 Handles Collections
FICO Score 8 distinguishes between different types of collections. It ignores small-dollar collections under $100, reducing the negative impact of minor debts. This approach prevents small financial mishaps from severely affecting the score.
Medical Debt: A Different Approach
FICO Score 8 treats medical debt more leniently. Recognizing that medical expenses are often unavoidable, it reduces the impact of unpaid medical bills on the overall score, offering a fairer assessment of credit risk.
The Role of Credit Card Usage in FICO Score 8
Responsible credit card usage is crucial. High balances and maxed-out cards can significantly lower your score. Regularly paying off balances and keeping utilization low are effective strategies to maintain a strong score.
How FICO Score 8 Treats High Balances
FICO Score 8 is sensitive to high credit card balances. Maintaining high balances can signal financial instability, lowering your score. Keeping balances low relative to credit limits is essential for a healthy score.
The Importance of Managing Revolving Credit
Revolving credit, primarily credit cards, plays a significant role in your FICO Score 8. Properly managing revolving credit, including timely payments and low balances, demonstrates financial responsibility and boosts your score.
Common Misconceptions About FICO Score 8
Many believe closing unused credit accounts boosts scores; however, this can shorten credit history and increase utilization rates, harming your score. Understanding such nuances helps in better score management.
How FICO Score 8 Affects Loan Approvals
FICO Score 8 is pivotal in loan approvals. Higher scores generally lead to better loan terms, including lower interest rates. Conversely, lower scores may result in higher rates or loan denials.
Impact on Mortgage Applications
For mortgages, FICO Score 8 plays a crucial role. Lenders use this score to determine loan eligibility and terms. A higher score can mean lower interest rates and more favorable loan conditions.
Car Loans and FICO Score 8
When applying for car loans, FICO Score 8 helps lenders assess risk. Higher scores often lead to better financing options, including lower interest rates and more favorable repayment terms.
Credit Cards and FICO Score 8
Credit card issuers rely heavily on FICO Score 8. A good score can lead to higher credit limits and lower interest rates, while a poor score can limit access to credit and increase borrowing costs.
How Lenders Use FICO Score 8
Lenders use FICO Score 8 to evaluate credit risk and make informed lending decisions. This score helps in determining creditworthiness and setting appropriate terms for loans and credit products.
Improving Your FICO Score 8
Improving your FICO Score 8 requires strategic financial behavior. Key strategies include paying bills on time, reducing outstanding debt, avoiding unnecessary credit inquiries, maintaining a healthy credit mix, and regularly monitoring your credit report.
Paying Bills on Time
Consistently paying bills on time is vital. Late payments can drastically lower your score, while a history of timely payments boosts it. Automating payments can help ensure punctuality.
Reducing Outstanding Debt
High levels of debt can negatively impact your score. Developing a plan to pay down outstanding balances can improve your score and overall financial health.
Avoiding New Credit Inquiries
Frequent credit inquiries can lower your score. Limit applications for new credit and avoid opening unnecessary accounts to maintain a strong score.
Maintaining a Healthy Credit Mix
A varied credit portfolio positively influences your score. Balancing different types of credit accounts demonstrates proficient credit management, benefiting your score.
Monitoring Your Credit Report
Regularly monitoring your credit report helps identify errors or fraudulent activity that could harm your score. Correcting inaccuracies promptly can protect and improve your score.
Tools and Resources for Tracking FICO Score 8
Several tools and resources are available for tracking your FICO Score 8. Credit monitoring services and financial apps provide insights and updates, helping you stay informed about your credit health.
The Future of Credit Scoring Models
Credit scoring models continue to evolve. Future iterations may incorporate alternative data points and advanced analytics to provide even more accurate assessments of credit risk.
Potential Changes and Upgrades to FICO Scores
Potential upgrades to FICO scores could include more comprehensive evaluations of financial behavior, offering a clearer picture of creditworthiness and enhancing lenders’ decision-making processes.
How FICO Score 8 Fits into the Bigger Financial Picture
FICO Score 8 is a critical component of your financial profile. Understanding its impact and managing it effectively can lead to better financial opportunities and a more secure financial future.
BOTTOM LINE
Mastering FICO Score 8 is essential for financial success. By understanding its components and implementing strategies to improve it, you can enhance your creditworthiness and achieve your financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I raise my FICO score 8?
To raise your FICO Score 8, focus on paying your bills on time, reducing your outstanding debt, and avoiding new credit inquiries. Regularly monitor your credit report for errors and maintain a healthy credit mix. Implementing these strategies can gradually improve your credit score.
Is 750 a good FICO 8 score?
Yes, a FICO Score 8 of 750 is considered very good. It indicates that you have a strong credit history and are likely to receive favorable loan terms and interest rates from lenders.
What is a FICO score 8 of 800?
A FICO Score 8 of 800 is excellent. This score places you in a top tier of creditworthiness, meaning you have a long history of responsible credit behavior. You are likely to receive the best loan terms and lowest interest rates.
Is FICO 8 or 9 higher?
FICO 8 and FICO 9 are different versions of the FICO credit scoring model. They are not directly comparable in terms of being higher or lower, as each uses slightly different criteria for calculation. However, both scores generally fall within the same numerical range.
What is the difference between FICO 5 and FICO 8?
FICO 5 and FICO 8 are different versions of the FICO credit scoring model. includes enhancements such as reduced impact from small-dollar collections and a higher sensitivity to high credit card usage. FICO 5 is an older version still used by some mortgage lenders.
What’s a good FICO score?
A good FICO score is typically considered to be between 670 and 739. Scores in this range suggest that you have a positive credit history and are a low credit risk.
Is a FICO score of 600 considered good?
No, a FICO score of 600 is considered fair. It suggests that you have some negative information on your credit report, which could make it more difficult to obtain credit at favorable terms.
How is FICO 8 calculated?
FICO 8 is calculated based on five main factors: payment history (35%), credit utilization (30%), length of credit history (15%), new credit (10%), and credit mix (10%). Each factor contributes differently to the overall score.
Is a 720 FICO 8 good?
Yes, a FICO Score 8 of 720 is considered good. It indicates that you have a solid credit history and are likely to receive favorable terms on loans and credit cards.
How do I know my FICO score?
You can obtain your FICO score through various financial institutions, credit card issuers, or by purchasing it directly from the FICO website. Some credit monitoring services also provide access to your FICO score.
How is a FICO score different from a credit score?
A FICO score is a specific type of credit score created by the Fair Isaac Corporation. While all FICO scores are credit scores, not all credit scores are FICO scores. Different scoring models, like VantageScore, use their own criteria to calculate credit scores.
Why does my FICO score say 8?
The “8” in FICO Score 8 indicates the specific version of the FICO scoring model being used. FICO periodically updates its scoring models to reflect changes in consumer credit behavior and to improve predictive accuracy.
What is the highest FICO score you can have?
The highest FICO score you can have is 850. Achieving this score requires impeccable credit management, including a long history of on-time payments, low credit utilization, and a diverse credit mix.
Why is my FICO score higher than my credit score?
Your FICO score may be higher than other credit scores because different scoring models use different criteria and algorithms to calculate scores. FICO scores may also weigh certain factors differently than other models like VantageScore.
What’s a good FICO score 9?
A good FICO Score 9 is typically considered to be between 670 and 739. This range suggests that you have a positive credit history and are a low credit risk.
Is FICO 8 good or bad?
FICO 8 itself is neither good nor bad; it is a credit scoring model. Your FICO Score 8 can be good or bad depending on the numerical value. Higher scores indicate good credit behavior, while lower scores suggest higher credit risk.
Can my bank give me my FICO score?
Yes, many banks and credit card issuers provide their customers with access to their FICO scores as part of their account services. Check with your bank to see if they offer this benefit.
Is a 900 credit score possible?
No, a 900 credit score is not possible under the FICO scoring model, which ranges from 300 to 850. Achieving a score close to 850 is the highest attainable goal.









